ARTICLE AD BOX
Last Updated:October 20, 2025, 13:00 IST
BrahMos-NG, a new supersonic cruise missile by India and Russia, will reach 4300 kmph and 800 km range, boosting Indian Army and Navy power
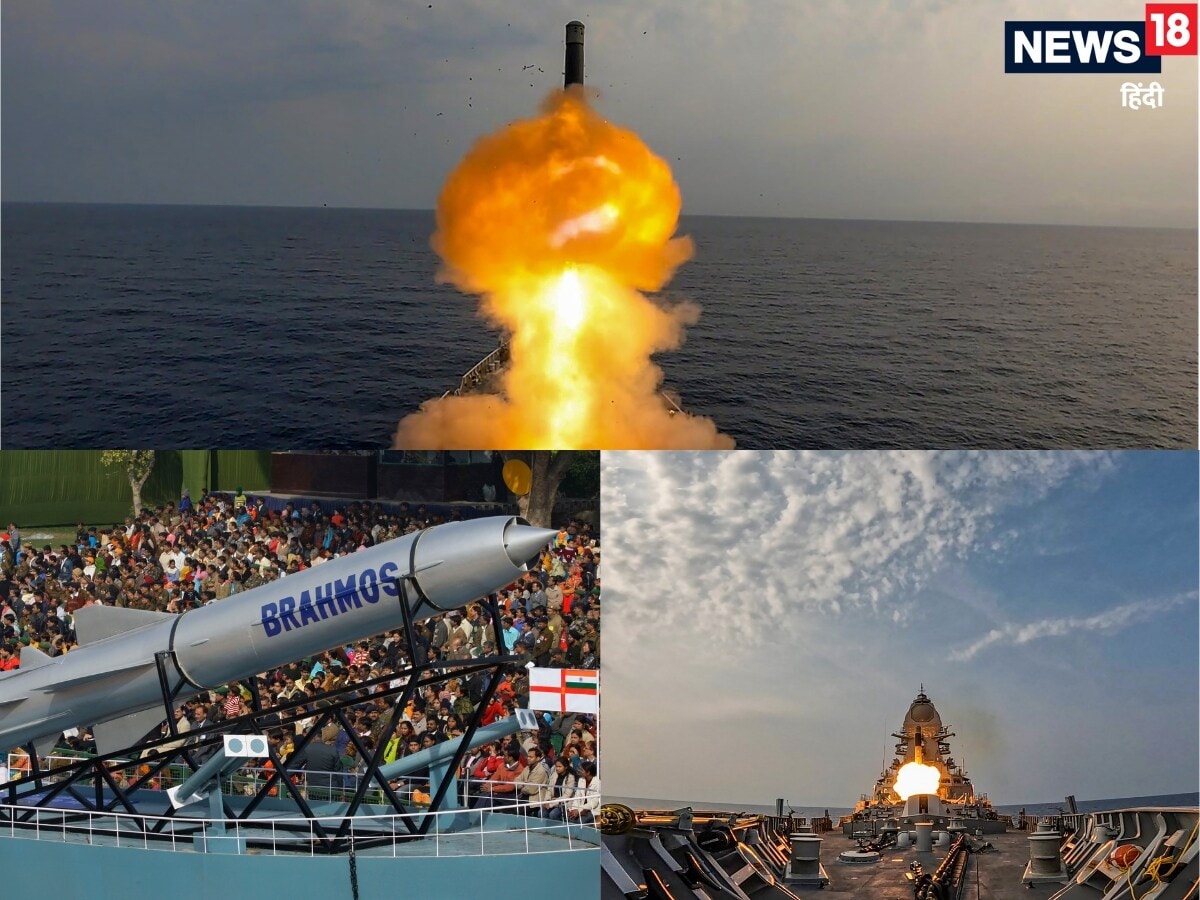

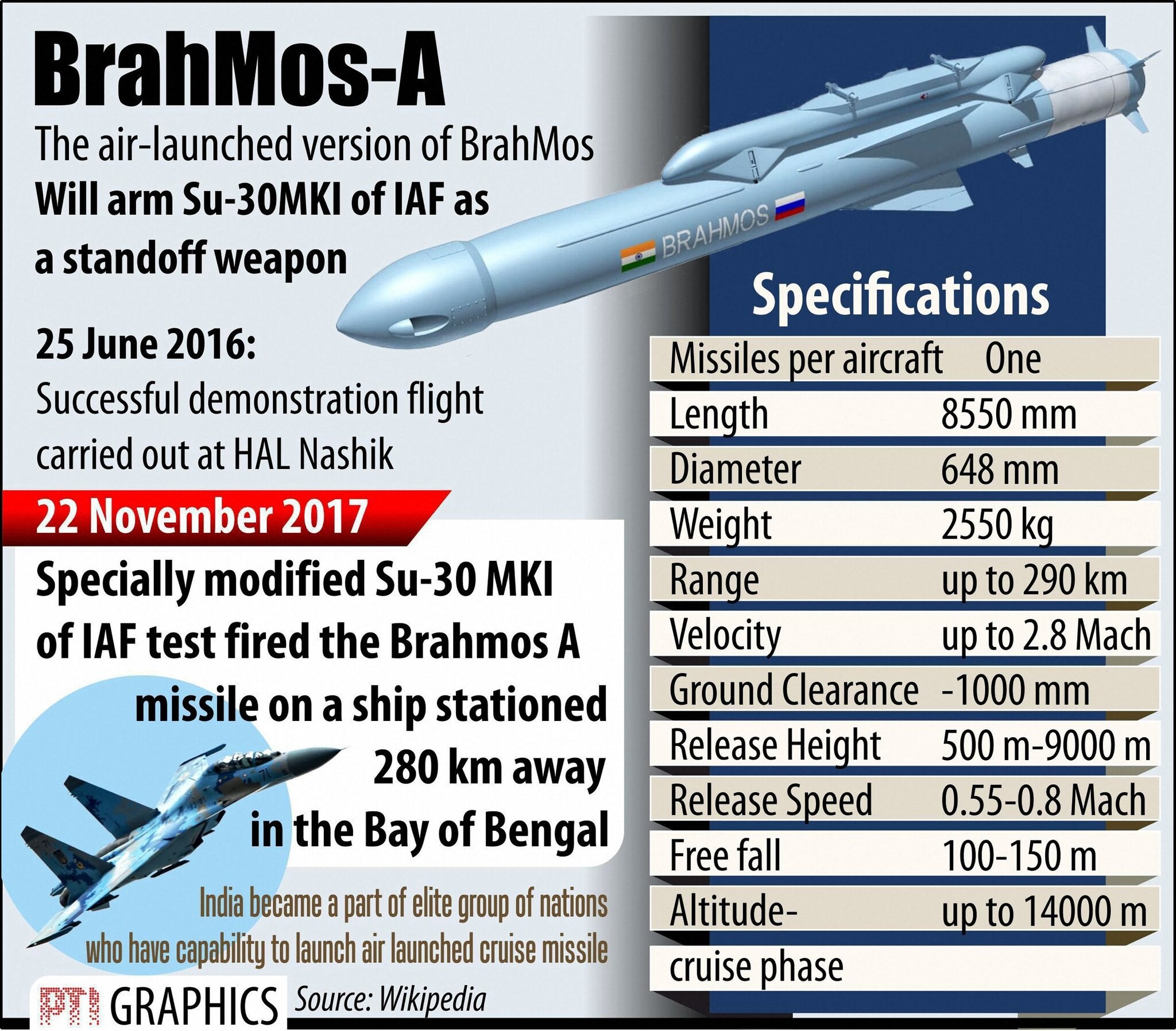
A new generation of the BrahMos supersonic cruise missile, considered one of India's most formidable precision-strike weapons, is in the advanced stages of development, signalling a major leap in defence capability. According to official sources, the upcoming variant, known as BrahMos-NG (Next Generation), is expected to achieve a top speed of over 4,300 kmph and extend its strike range to 800 kilometres, nearly double that of the current operational version. (PTI Photo)
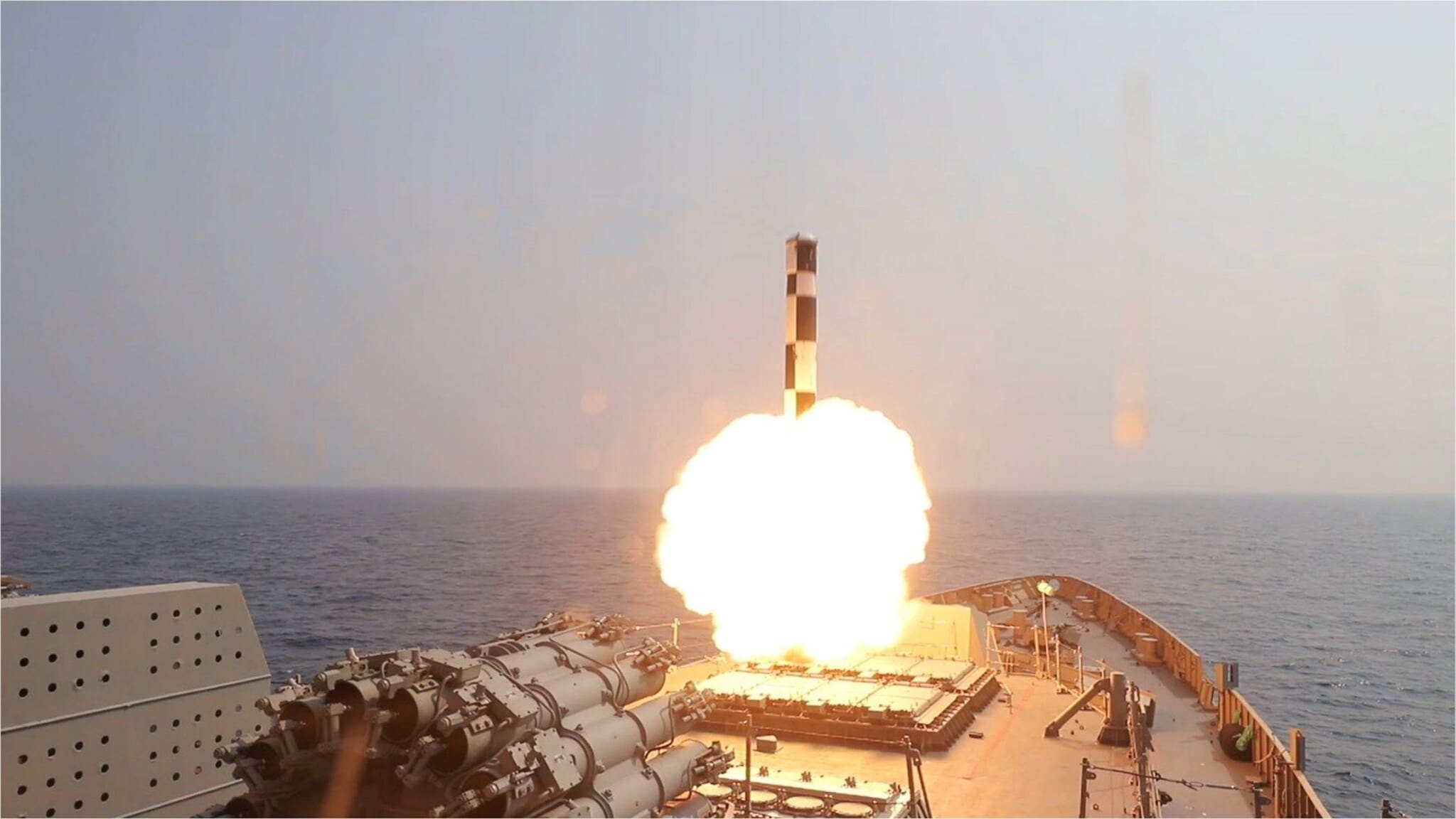

Developed jointly by India and Russia, the BrahMos missile system has already earned global recognition for its accuracy and destructive capability. Its effectiveness was notably demonstrated during Operation Sindoor, when the Indian Air Force launched the air-based BrahMos-A from a Sukhoi-30MKI fighter jet, striking targets deep within enemy territory from a stand-off distance. (PTI Photo)
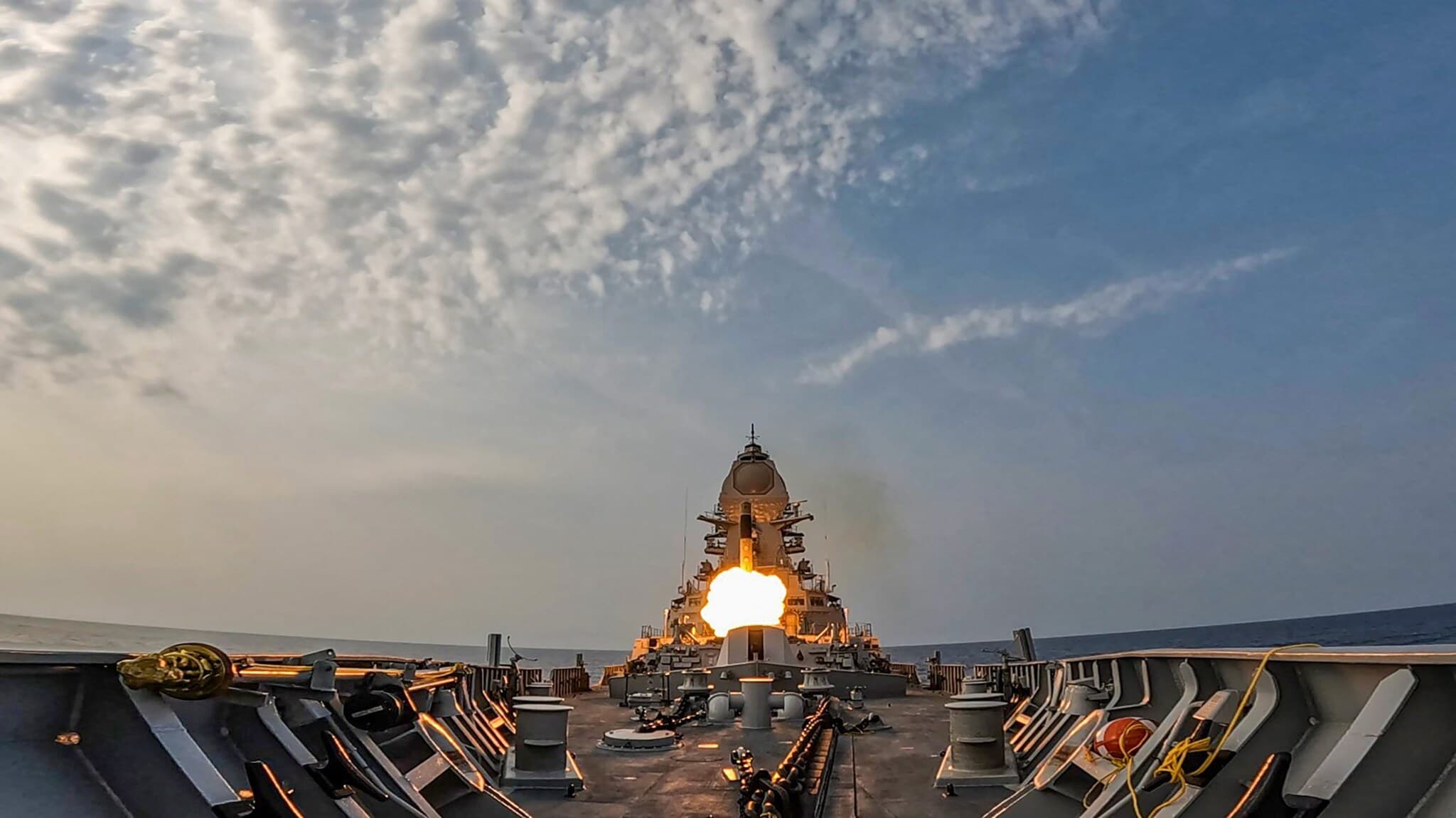

The existing BrahMos missile currently operates with a range between 450 and 490 km, while earlier export versions were capped at 290 km due to international regulations. The BrahMos-NG promises to elevate this capability significantly, enhancing speed, range and lethality. (PTI Photo)
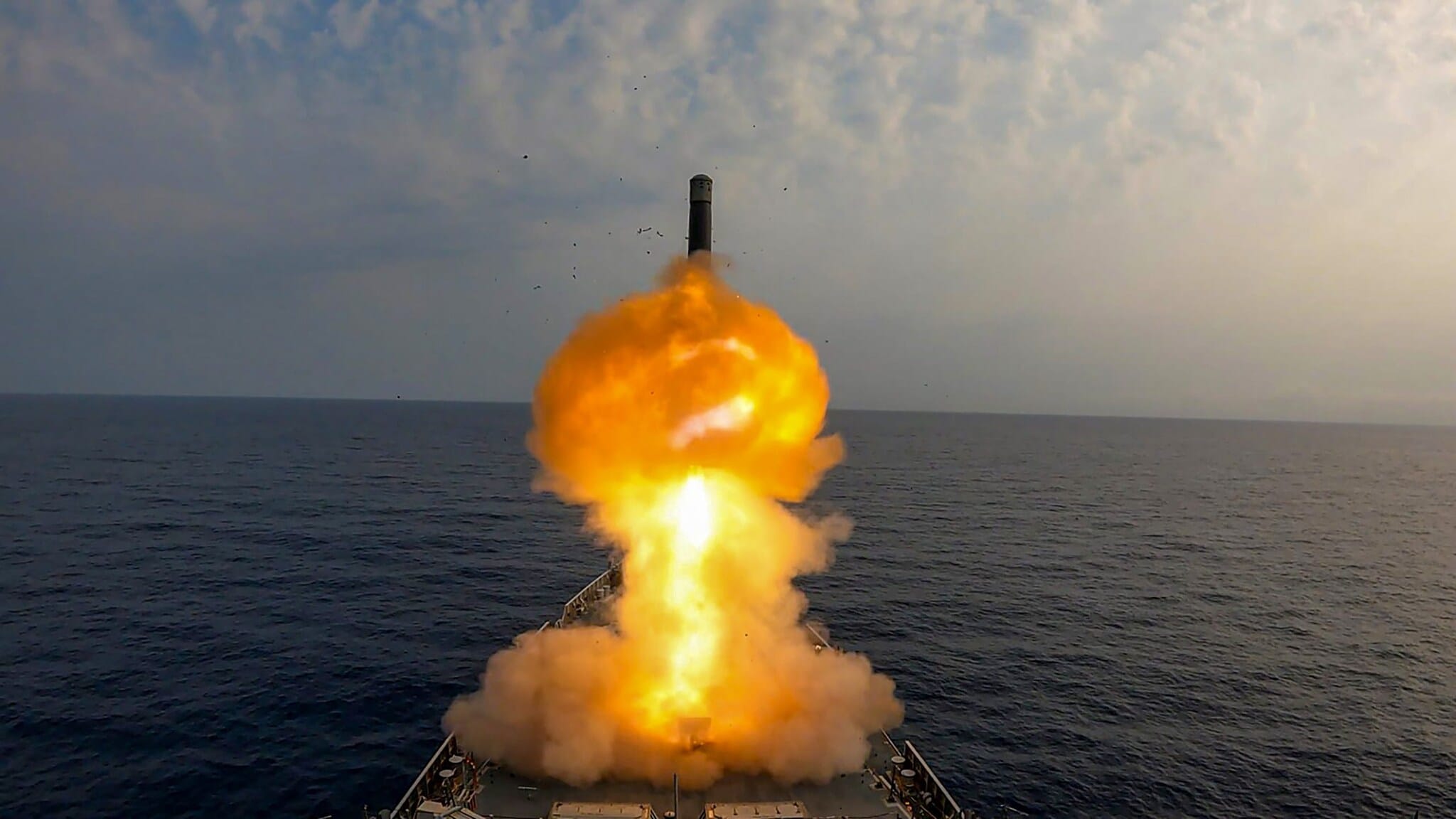

Defence officials have confirmed that the ramjet engine and navigation systems, including an upgraded Inertial Navigation System (INS) combined with external Global Navigation Satellite System (GNSS) support, are undergoing rigorous testing to ensure high accuracy and resilience against electronic jamming. (PTI Photo)
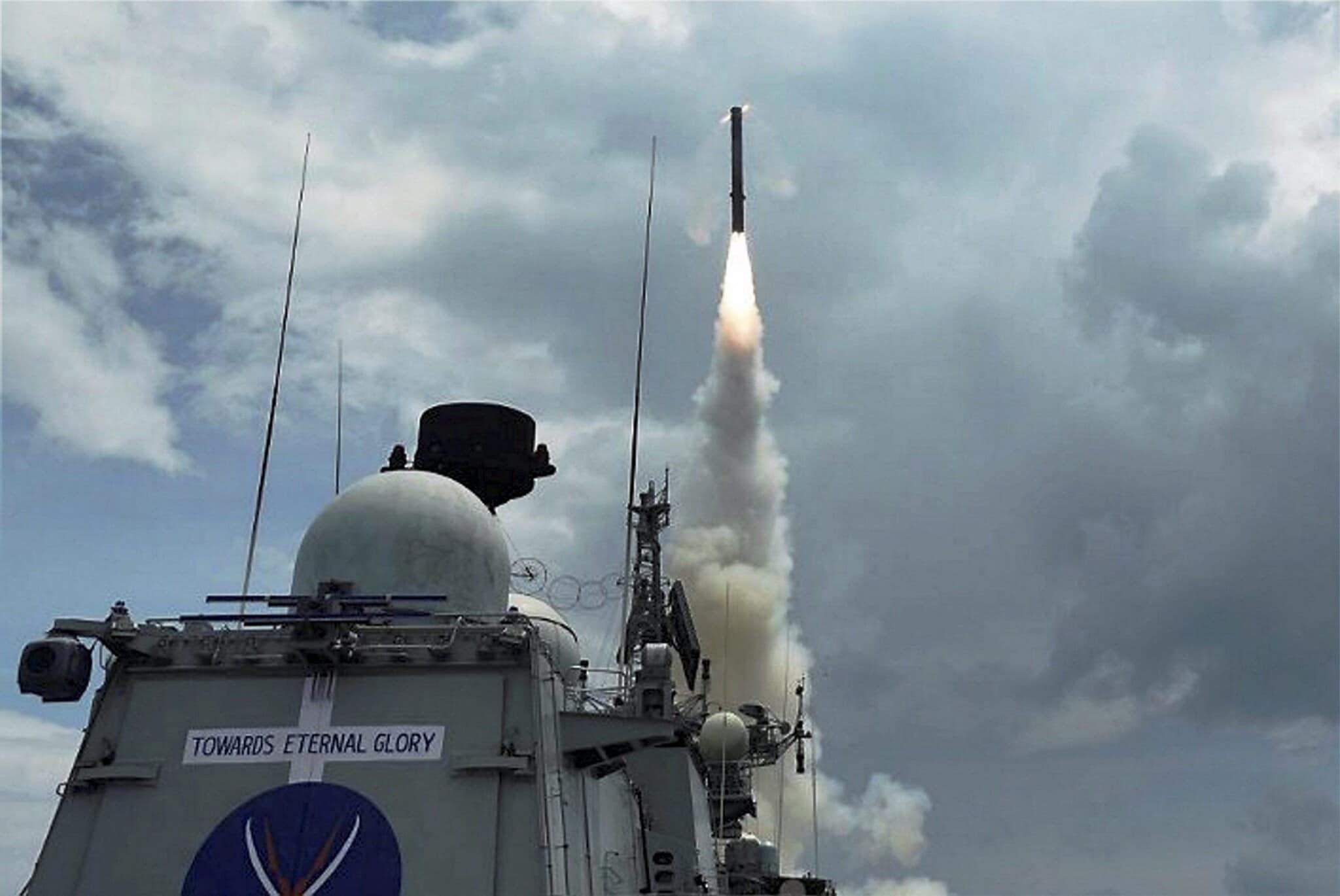

Sources indicate that the Indian Army and Navy will be the first to receive the upgraded systems. Existing launch platforms equipped with the 450-km variant can be modernised for the 800-km version through software updates and interface adjustments in the fire-control systems. The air-launched variant, however, will take slightly longer to enter service due to additional aerodynamic and integration requirements with fighter aircraft. The missile is expected to be inducted into the armed forces within the next two years, subject to successful completion of ongoing trials. (PTI Photo)
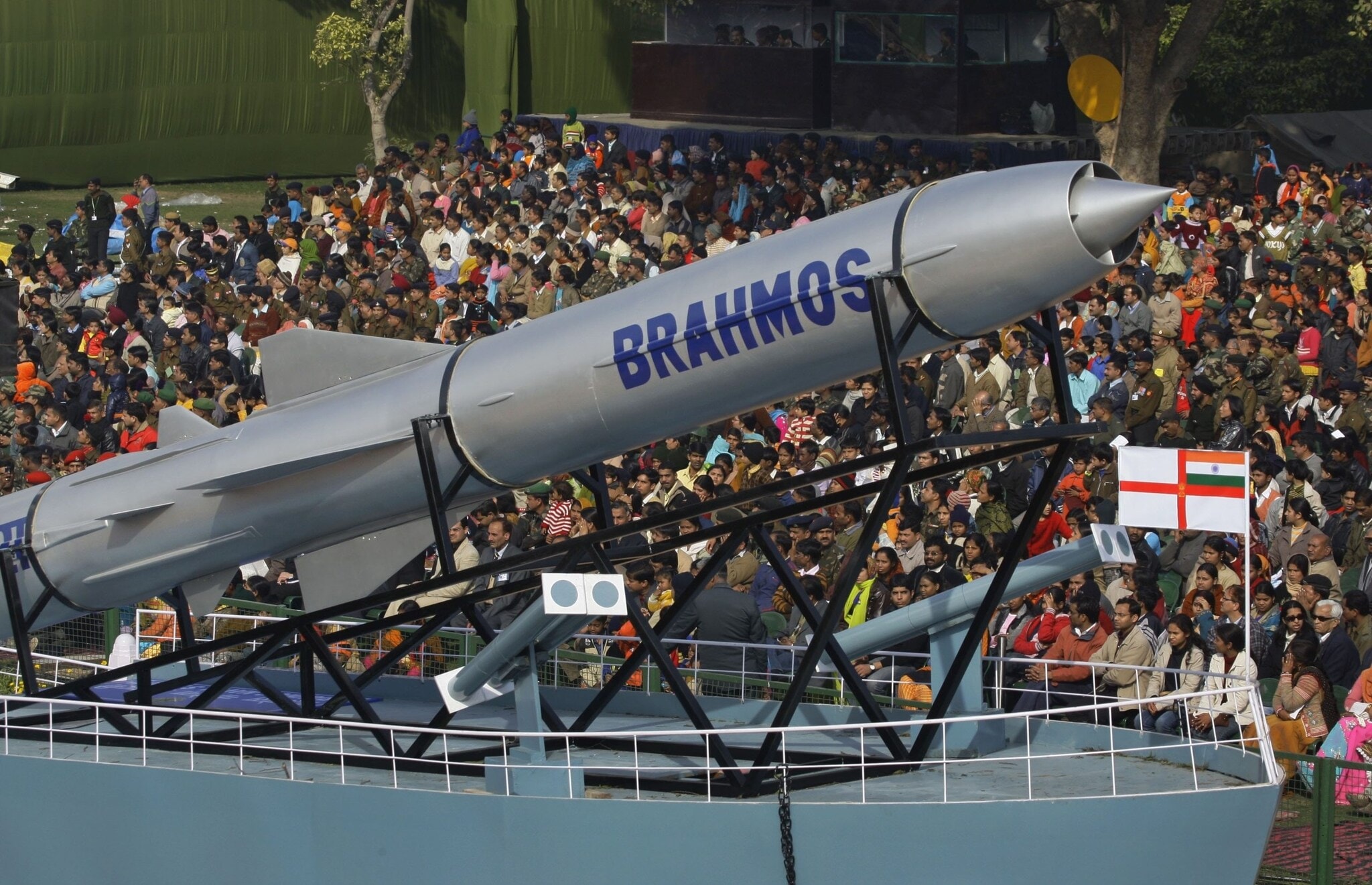

Parallel to the BrahMos-NG programme, the Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO) is also upgrading other indigenous weapon systems. The Astra Mark-2 air-to-air missile, currently possessing a range of 160 km, is being enhanced to exceed 200 km, with production slated for 2026–27. The Indian Air Force has already approved the procurement of 700 Astra Mk-2 missiles for its Su-30MKI and Tejas aircraft. (PTI Photo)
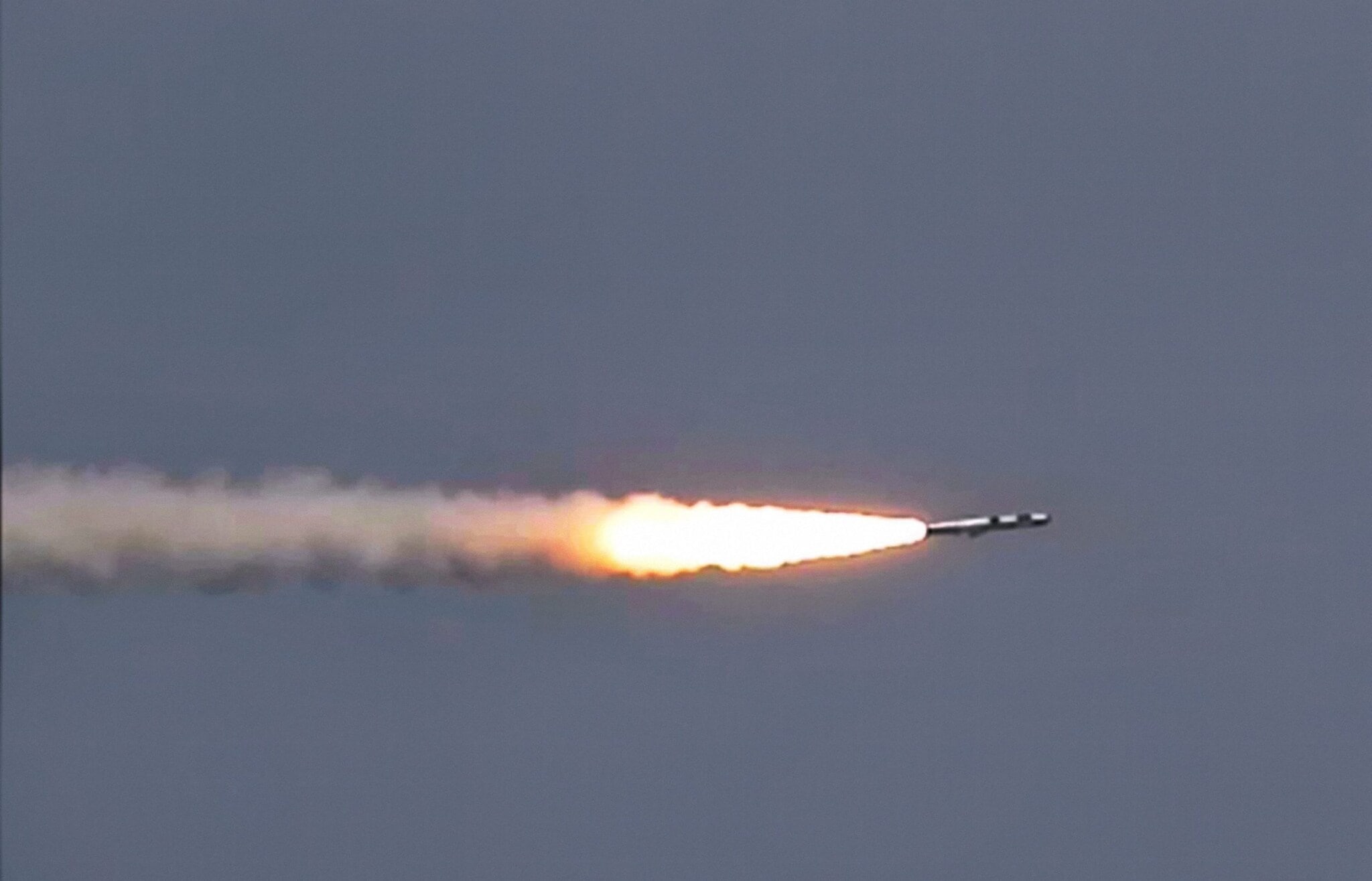

The growing international interest in the BrahMos system reflects its global strategic relevance. Several nations have approached India for potential defence procurement, following its combat-proven performance and precision strike capabilities. Experts believe the combination of 800-km BrahMos-NG and 200-km-plus Astra missiles could significantly alter South Asian strategic equations, bolstering India's deterrence posture and enhancing its ability to conduct deep surgical strikes. Defence Minister Rajnath Singh has described the BrahMos programme as a symbol of 'Atmanirbhar Bharat' (self-reliant India). (PTI Photo)
Vertical-launch BrahMos systems have already been deployed across numerous warships of the Indian Navy, while the Defence Acquisition Council (DAC) has cleared multiple contracts, cumulatively worth several thousand crores. This cements BrahMos as the central conventional long-range precision strike weapon in the military's arsenal. (PTI Photo)
News Photogallery india BrahMos-NG: India's Most Lethal Missile Yet At 4,300 KMPH And 800-KM Range

 1 day ago
7
1 day ago
7








 English (US) ·
English (US) ·