ARTICLE AD BOX
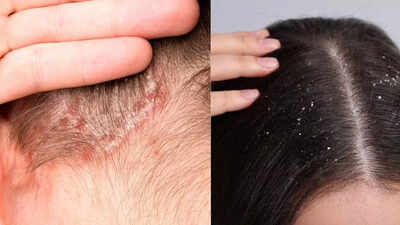
If your scalp is itchy, flaky, or irritated, it can be difficult to know whether it’s simple dandruff or a more serious condition like scalp psoriasis. Both problems share similar symptoms such as itching and visible flakes, but they differ in their causes, severity, and treatment.
Dandruff is generally mild, temporary, and manageable with over-the-counter shampoos, often linked to oily skin, fungal overgrowth, or irritation. In contrast, scalp psoriasis is a long-lasting autoimmune condition that causes thick, scaly patches and may spread beyond the scalp. Identifying the difference is key to finding the right care and long-term relief.
Understanding how dandruff and scalp psoriasis are different from each other
Dandruff
Dandruff is one of the most common scalp conditions worldwide.
It occurs when the scalp sheds flakes of dead skin, often accompanied by itching. While not dangerous, dandruff can be persistent and embarrassing.
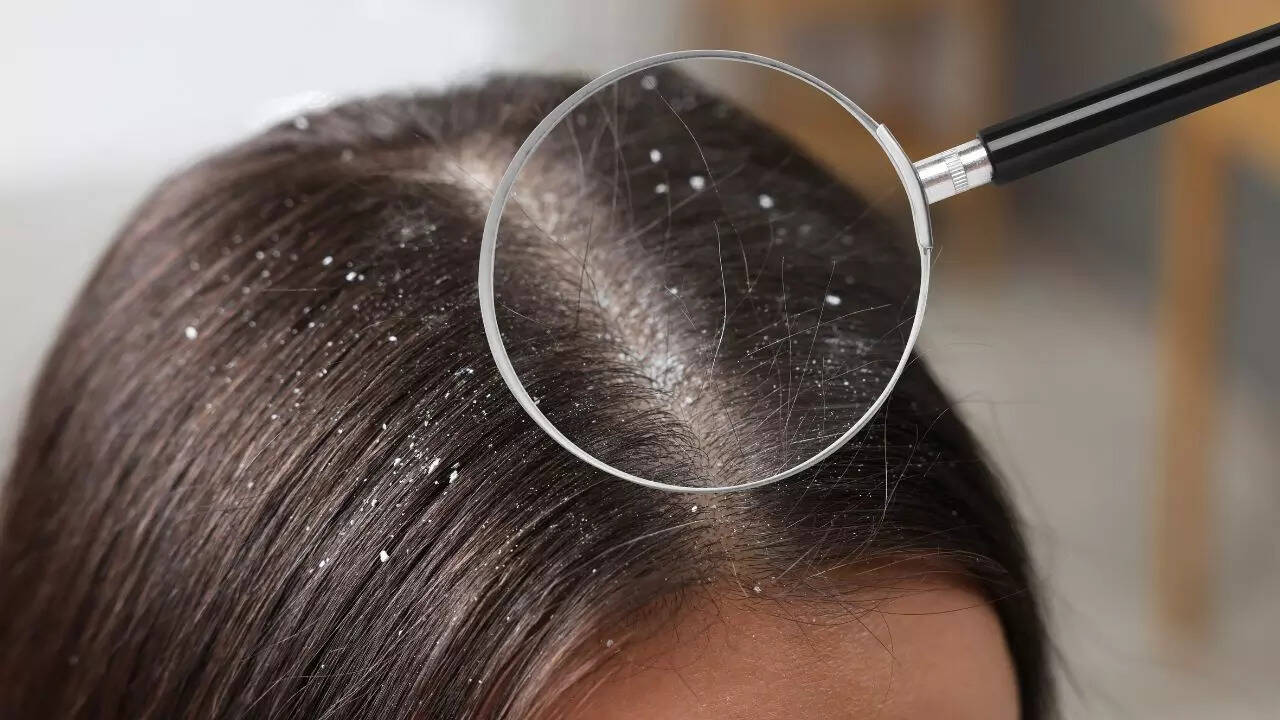

White or yellow flakes on hair and clothing.Itchy but not usually painful.Comes and goes depending on scalp condition or product use.Not contagious.
Scalp psoriasis
Scalp psoriasis is a chronic autoimmune condition where the immune system mistakenly attacks skin cells, causing them to multiply too quickly.
This leads to thick, scaly patches that often extend beyond the scalp.
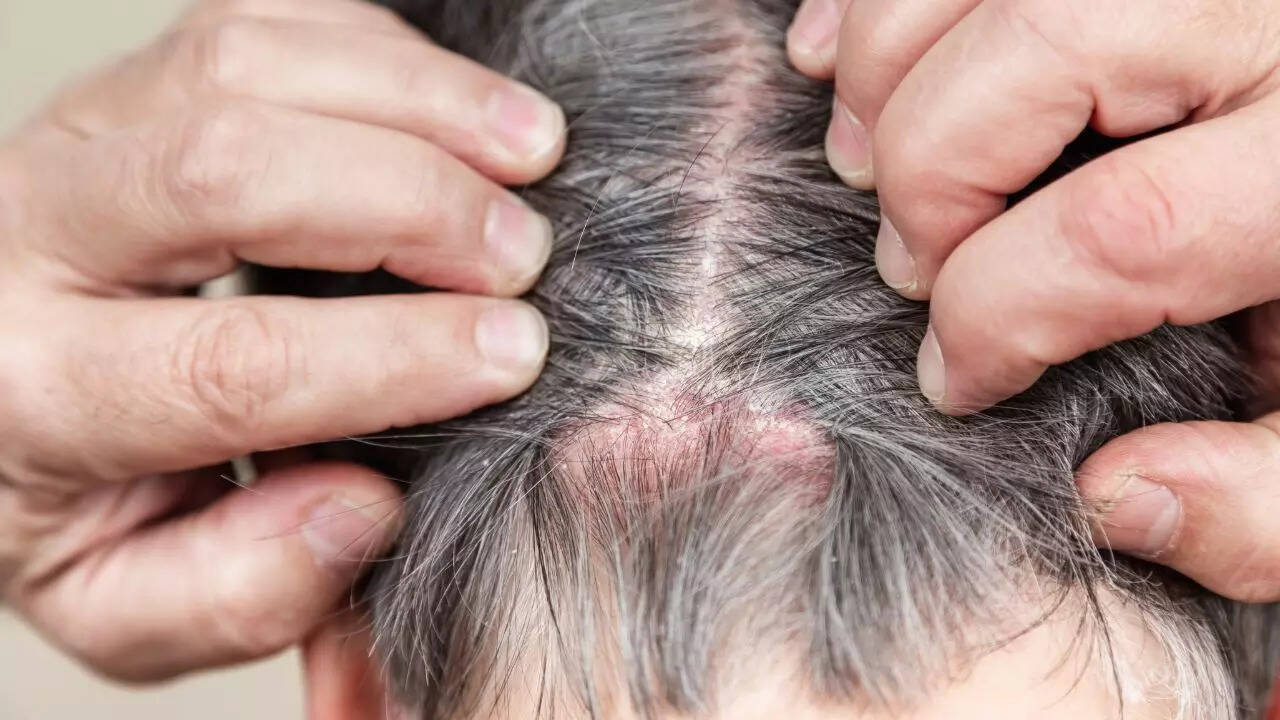
- Chronic condition: Symptoms flare up and subside but rarely disappear completely.
- Scaly patches: Appear silver, powdery, or thick, sometimes painful.
- Spreads beyond the scalp: Patches may appear on the forehead, neck, ears, elbows, knees, and back.
- Autoimmune link: Caused by immune system dysfunction rather than lifestyle factors.
Unlike dandruff, scalp psoriasis is not just a cosmetic issue but a medical condition that requires proper diagnosis and management.
Comparing the causes of dandruff and scalp psoriasis
Causes of dandruff According to a study in ResearchGate, common causes of dandruff are:
- Seborrhoeic dermatitis: Oily, itchy, irritated skin that flakes off.
- Contact dermatitis: Reactions to hair care products such as shampoos, gels, or dyes.
- Fungal overgrowth: Particularly Malassezia, a yeast that thrives on scalp oils.
- Poor hygiene: Infrequent hair washing allows oil and skin to build up.
- Dry skin: Small, white flakes across the scalp and often the rest of the body.
- Hormones: Men are more prone to dandruff due to male hormone influence.
- Weakened immunity: People with compromised immune systems (e.g., HIV) may be more susceptible.
Causes of scalp psoriasisAccording to a study in NHS, scalp psoriasis, can be caused due to the following factors:
- Immune system dysfunction: Psoriasis is an autoimmune condition where overactive immune cells trigger rapid skin cell turnover.
- Genetics: A family history of psoriasis increases the risk significantly.
- Stress: Physical or emotional stress can trigger flare-ups or worsen existing symptoms.
- Infections: Throat infections (e.g., strep throat) and other illnesses can provoke outbreaks.
- Hormonal changes: Fluctuations during puberty, pregnancy, or menopause can influence flare-ups.
- Lifestyle triggers: Alcohol consumption, smoking, and poor diet are known to worsen psoriasis severity.
- Weather conditions: Cold, dry climates can make symptoms more pronounced.
Common symptoms of dandruff and scalp psoriasis compared
Although dandruff and scalp psoriasis both cause visible flakes and itching, the type and severity of symptoms are quite different.1. Itching and flaking
- Dandruff usually produces loose, white or yellow flakes that fall easily onto clothing. The itching can be bothersome but is rarely severe.
- Scalp psoriasis creates thick, silvery scales that stick to the scalp. Itching may be intense and often accompanied by burning or soreness.
2. Redness and irritation
- Dandruff causes mild redness or greasy patches due to excess oil production.
- Psoriasis leads to inflamed, raised plaques that may crack or bleed.
3. Spread beyond the scalp
- Dandruff is confined to the scalp and does not spread elsewhere.
- Psoriasis can extend to the forehead, ears, neck, elbows, knees, and even nails.
4. Pain or bleeding
- Rare in dandruff.
- Common in psoriasis when scales are scratched off or the skin cracks.
Risk factors for each condition
Dandruff
- Oily scalp: Excess sebum provides a breeding ground for yeast.
- Fungal overgrowth: Malassezia yeast thrives on natural scalp oils.
- Age and hormones: Dandruff is more common in teenagers and adults, especially men, due to hormonal influences.
- Poor hygiene or infrequent hair washing: Allows oil and dead skin to build up.
- Stress and climate: Flare-ups are often worse in winter or during stressful periods.
Scalp psoriasis
- Genetics: A strong family history of psoriasis increases risk.
- Autoimmune factors: The immune system mistakenly accelerates skin cell turnover.
- Stress: Known to trigger or worsen flare-ups.
- Medications: Certain drugs can aggravate psoriasis.
- Lifestyle triggers: Alcohol, smoking, and infections may contribute to flare-ups.
- Other health conditions: People with obesity, diabetes, or inflammatory disorders are at higher risk.
Diagnosis: Dandruff vs scalp psoriasis
A doctor can often diagnose the difference simply by examining your scalp. However, in some cases, they may take a small sample of skin for microscopic examination.
- Dandruff is identified by loose flakes, oily patches, and itchiness.
- Scalp psoriasis is diagnosed by thicker, inflamed patches that may extend beyond the scalp.
If over-the-counter dandruff treatments fail, it’s important to see a dermatologist to rule out psoriasis or other conditions.
Key differences between dandruff and scalp psoriasis
| Feature | Dandruff | Scalp psoriasis |
| Cause | Fungal overgrowth, oil, or skin irritation | Autoimmune disorder |
| Appearance | White or yellow flakes, loose | Thick, silver, scaly patches |
| Duration | Comes and goes | Chronic, long-lasting |
| Spread | Limited to scalp | Extends beyond scalp |
| Severity | Mild discomfort | Can be painful, inflamed, severe |
| Treatment | OTC shampoos, hygiene | Prescription medicines, long-term care |
Disclaimer: This article is for informational purposes only and does not constitute medical advice. Always consult a qualified healthcare professional before making any changes to your health routine or treatment.Also read | How often should you replace your toothbrush, towel, makeup sponge, and other personal care essentials



.png)
.png)
.png)
















 6 days ago
4
6 days ago
4







 English (US) ·
English (US) ·