ARTICLE AD BOX
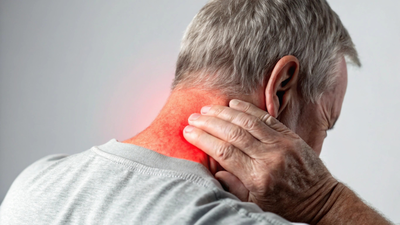
Chronic inflammation is now being viewed as a sneaky culprit that affects up to half of adults globally. Modern science shows 60 % of global deaths are attributed to diseases linked with chronic inflammation, and people silently suffer from low-grade, chronic inflammation and never even know it.
Unlike acute inflammation, which prompts the body to heal an injury or infection, chronic inflammation gradually degrades tissue, organs, and the nervous system over days, weeks, and even months. It is more and more associated with many diseases such as heart disease, diabetes, liver disease, and even some types of cancer. Because it's common and can be extremely bad, though, chronic inflammation remains underreported, earning the nickname of "silent epidemic".
What is chronic inflammation
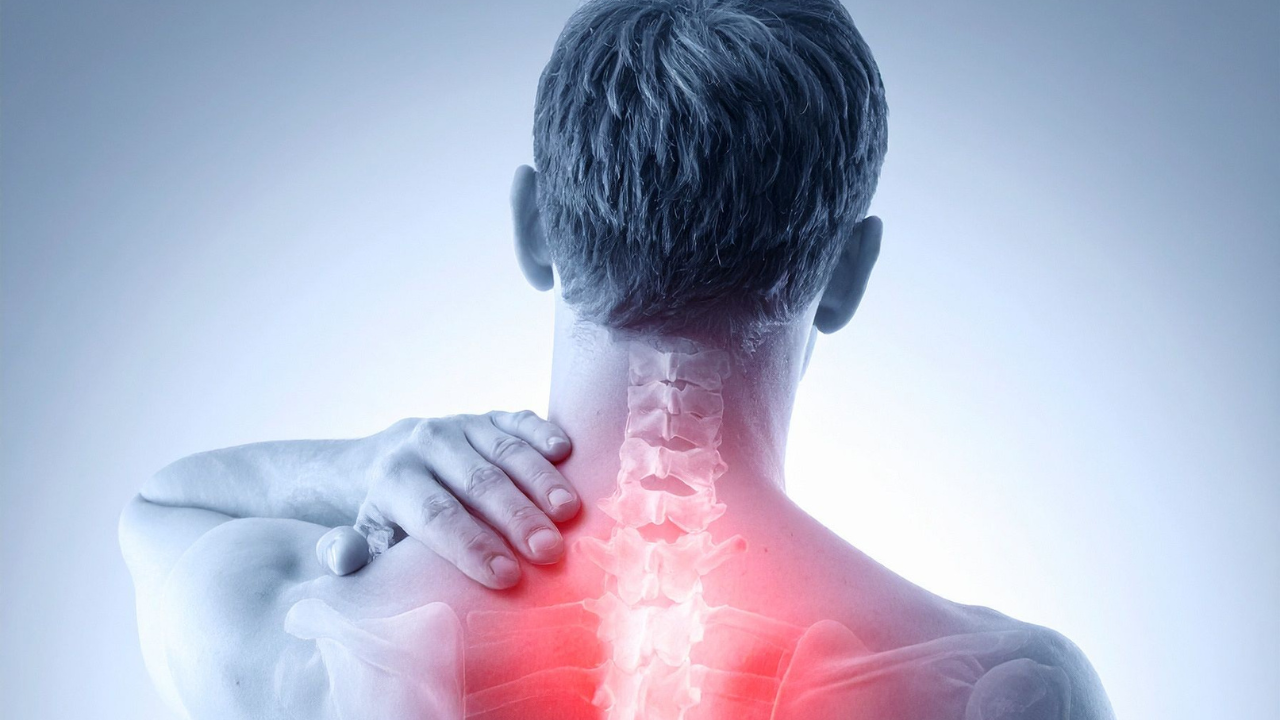
Chronic inflammation occurs when the body's immune system remains in a state of ongoing activation but, instead of being tuned into existing threats, the immune response goes haywire, spewing out molecules that increasingly damage tissue and cells. Over time, this leads to oxidative stress, organ malfunction, and increased vulnerability to disease. Malnutrition, poor sleep, stress, sedentary lifestyles, and environmental pollutants all can trigger this chronic inflammation.
According to a study in NCBI in 2014, nearly 60 % of Americans had at least one chronic condition. In that same estimate, 42 % had more than one chronic condition. Also cited: 12 % of adults had five or more chronic conditionsThe research also states that “worldwide, 3 of 5 people die due to chronic inflammatory diseases,” meaning 60 % of global deaths are attributed to diseases linked with chronic inflammation.
The root cause of all diseases
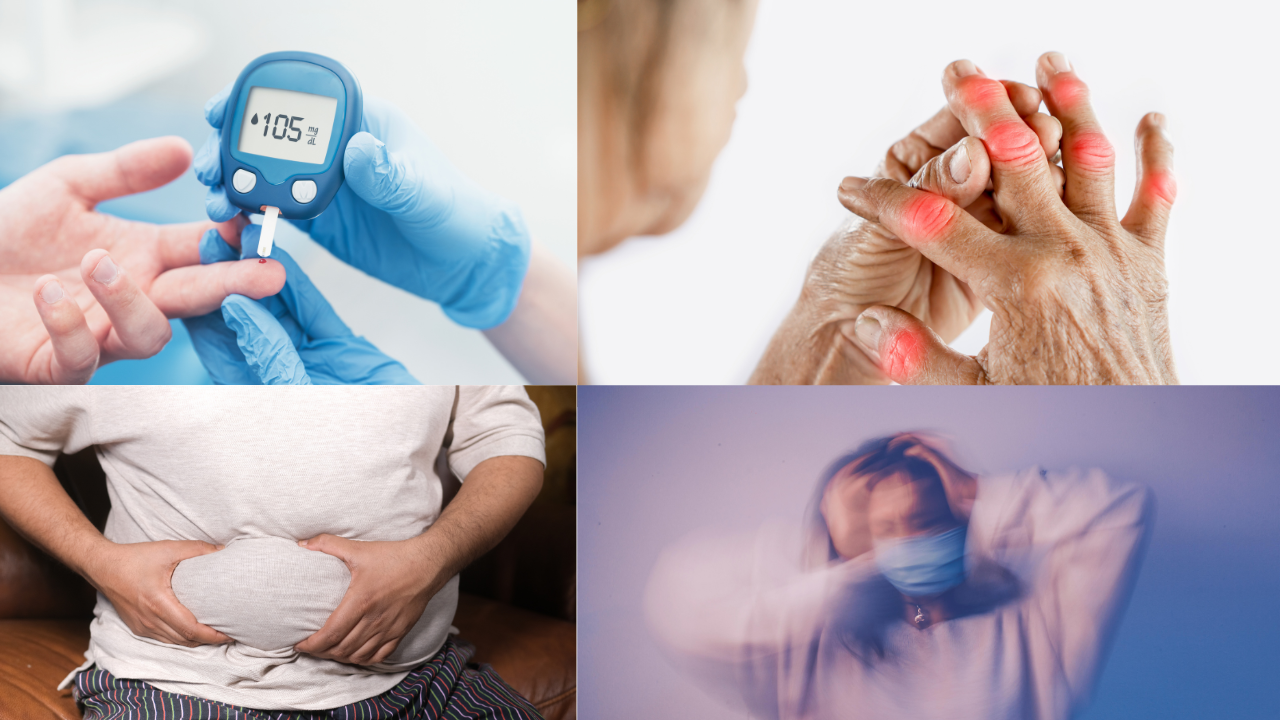
Medical research still points to chronic inflammation as the source of most prevalent and disabling diseases.
Cardiovascular disease, type 2 diabetes, obesity, liver disease, autoimmune diseases, and even neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer's have strong associations with inflammation. Body inflammation over time damages blood vessels, nerves, and organs increasingly, creating fertile soil for disease spread.
While diet and drug may manage symptoms, it must heal inflammation at the source in order to prevent permanent damage.
How does chronic inflammation work in the body
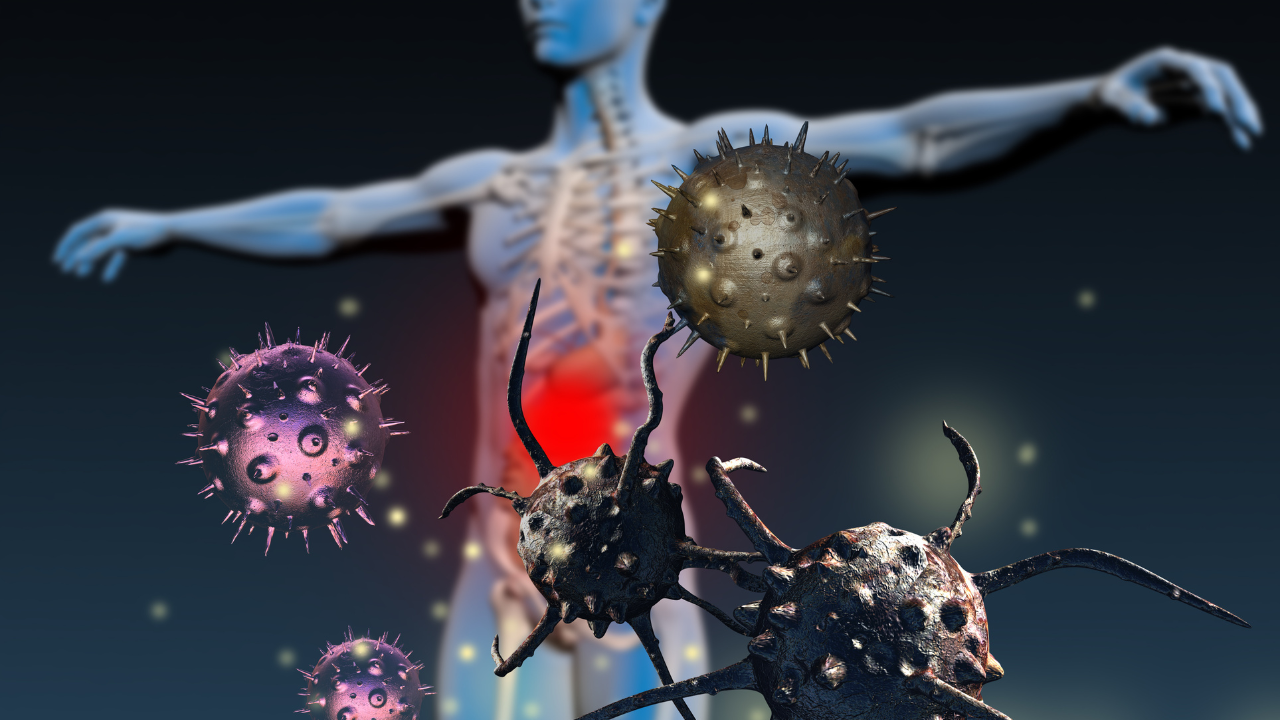
Unlike acute inflammation, which is a short-term and beneficial reaction, chronic inflammation lingers and becomes destructive over time. It begins with immune cells like macrophages, T-cells that release inflammatory signals known as cytokines, which are meant to combat perceived threats.Over time, this ongoing immune activity causes tissue damage. The immune cells release reactive oxygen species and enzymes that harm cells and structures in affected areas.
As the body tries to repair this damage, it often leads to fibrosis, or the accumulation of scar tissue, which further impairs normal tissue function.
Symptoms that are frequently overlooked
Chronic inflammation never produces showy symptoms at first, and therefore most individuals do not even realize that they have it. The subtle symptoms could be fatigue, gastrointestinal distress, unexplained weight gain or loss, musculoskeletal ache, or recurring skin problems.
The signs are generally linked to stress, aging, or mild diseases, and the disease is not treated promptly. Periodic examinations by the doctor, lab exams on inflammatory markers, and lifestyle factors in mind can capture inflammation before it progresses to worse diseases.
How to manage chronic inflammation
Inflammation needs to be addressed on various fronts, diet plays a role: Antioxidants, omega-3 fatty acids, and fiber all have anti-inflammatory effects, and processed foods, added sugar, and heavy drinking potentially exacerbate it.
Adequate sleep, stress management, and routine exercise all decrease inflammatory markers. Early treatment, besides advice from health professionals, can decrease long-term risk and immensely improve quality of life.
A call to awareness
Influencing the majority of adults, chronic inflammation is not visible when health is discussed. Knowing its signs, understanding why it occurs, and how to prevent it will prevent it from developing into frank disease. Emphasis on inflammation being a quiet but controllable foe empowers the patients to regain control over their good health and be free from the imbalance of having to live with numerous chronic diseases.
The stealthy price of this stealth killer emphasizes that anti-inflammation is not merely a health concern but a necessity in lifestyle.

 2 hours ago
4
2 hours ago
4









 English (US) ·
English (US) ·