ARTICLE AD BOX
Image credits:: Getty Images
The heart is the most vital organ in the human body. Out of all the organs that are essential for human life, the heart tops the list. However, it is also one of the most vulnerable organs susceptible to a variety of health risks due to harmful lifestyle habits.One of the rare yet damaging conditions that can happen to the heart is heart cancer or cardiac tumour. According to the European Society of Cardiology (ESC), they're found in less than 1 out of every 2000 autopsies. It occurs when diseased cells grow out of control on or near the heart and form a tumour.There are two types of heart tumours- primary and secondary. Primary heart tumours are abnormal growths in your heart and are very rare.
They can either be cancerous or noncancerous. 75% of them are benign and only 20% can be malignant. Secondary heart tumours spread to the heart from nearby organs. While it is 40 times more common than primary cardiac tumours, it is still relatively uncommon.
What are the symptoms of heart cancer?
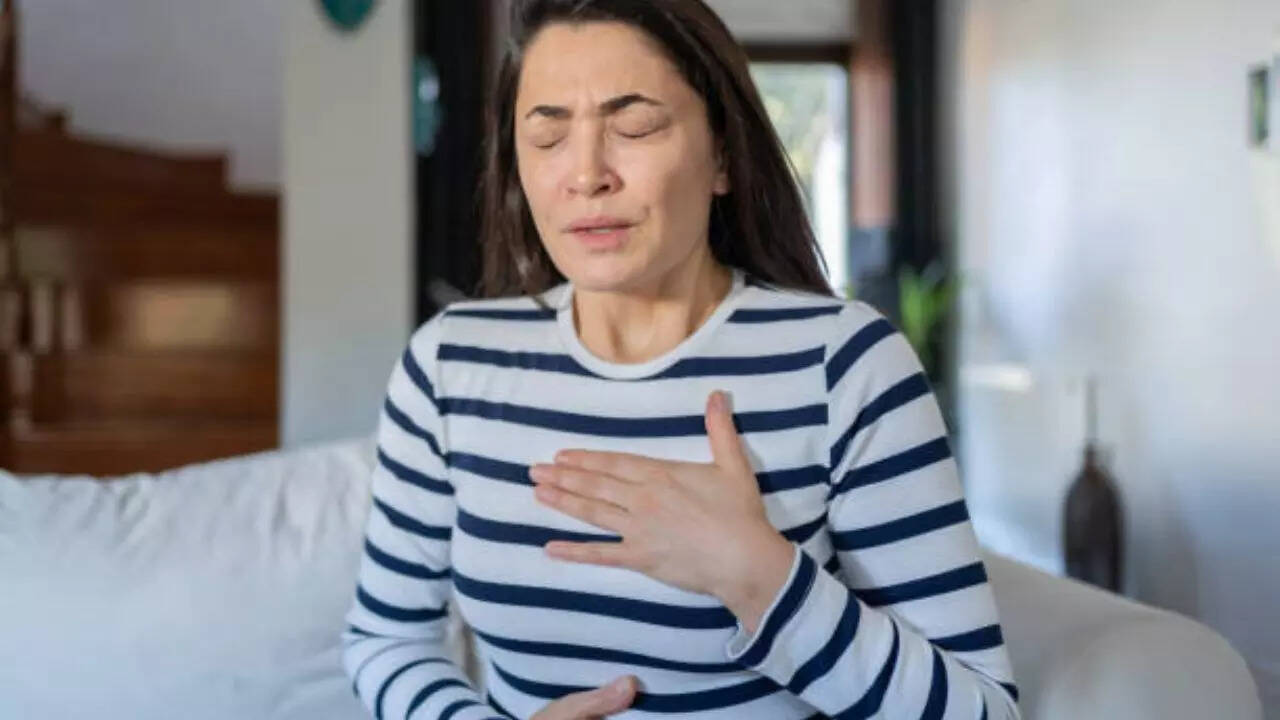

Image credits: Getty Images
The symptoms of heart cancer vary as per the type, size and location of the tumour. However, some common symptoms include chest pain, irregular heartbeat, shortness of breath, fatigue and weakness, swelling in legs and arms and fainting or dizziness.
There can also be some symptoms similar to an infection such as fever and chills, fatigue, night sweats, weight loss and joint pain.
What are the risk factors of heart cancer?
There are certain risk factors that can lead to heart cancer. As per age, heart cancer occurs mostly in adults, babies and children. It can also be hereditary and due to a poorly functioning immune system. There are also chances of genetic cancer syndromes where children with a rhabdomyoma have tubular sclerosis, a syndrome caused by a mutation in the DNA.
How is heart cancer diagnosed?
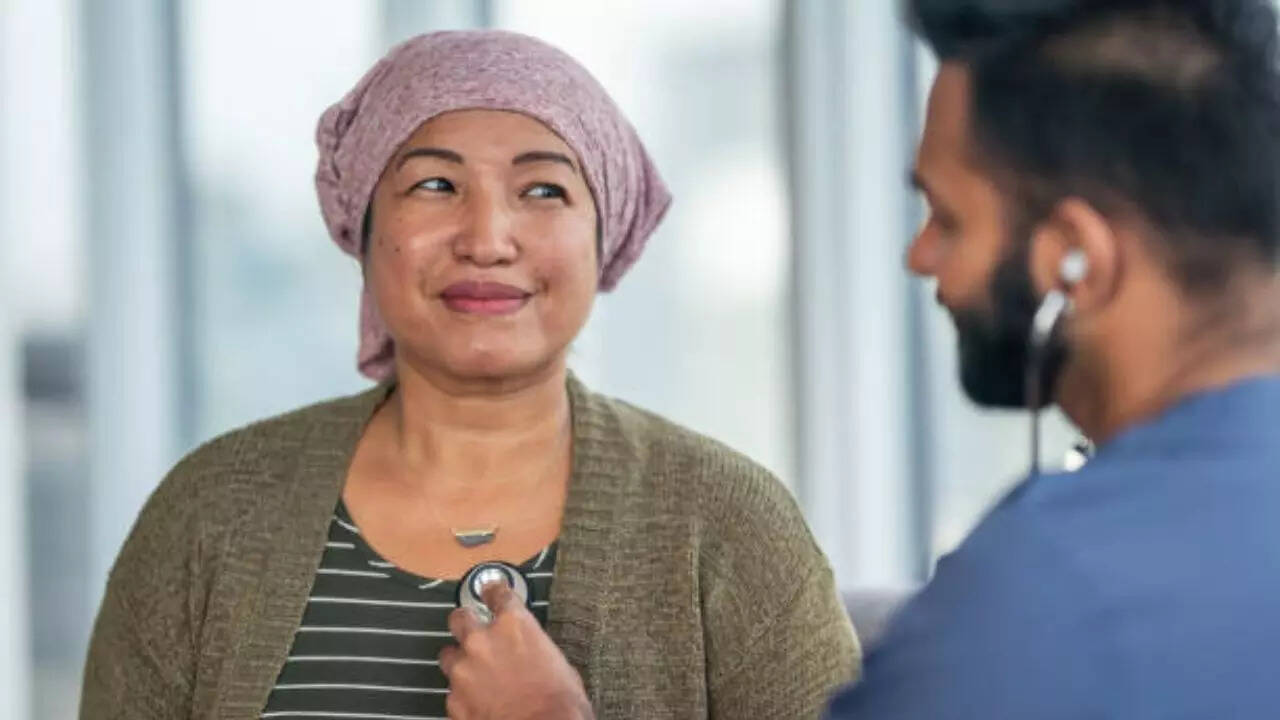

Image credit: Getty Images
With heart cancer being rare and the symptoms matching other heart conditions, the disease can be hard to diagnose. It is identifiable with the help of an Echocardiogram, a test that uses sound to create a moving image showing the structure and function of the heart. A CT scan can help differentiate between benign and malignant tumours, and an MRI provides more detailed images of the tumour to help doctors determine the type.
How is heart cancer treated?
Treatment options for heart cancer include surgery to remove the tumour, radiation therapy to shrink the tumour and chemotherapy drugs can be prescribed to target cancer cells and prevent further growth. A heart transplant can also be an option. Disclaimer: The information provided in this article is for general educational and informational purposes only and should not be construed as medical advice. If you are experiencing symptoms or have health concerns, please consult a licensed medical practitioner promptly.



.png)
.png)
.png)
















 4 hours ago
5
4 hours ago
5







 English (US) ·
English (US) ·